The name of such a disease is based on itvaricose veins of lower limbs, the Latin word "varicis" lies in it. It is translated as "bloating", which fully reflects the main symptom of this pathology, which is characterized by an abnormal expansion of the veins. It is accompanied by other, no less unpleasant manifestations in the form of impaired blood flow and valve dysfunction.
The medical statistics are relentless: the disease has affected a large part of the world's population! Thus, the clinical manifestations of varicose veins, expressed to varying degrees, are found in almost 90% of women and more than 65% of men. Unfortunately, the disease is getting younger and younger – and it is now being reported that it is even being detected in school-aged children!
If more than 80% of the listed symptoms occur, we strongly recommend that you consult a doctor for advice.
Varicose veinsthe disease of the veins, the clinical manifestations of which are the expansion and abnormal tortuosity of the veins, with the formation of venous nodes, and the subsequent progression of the symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency, of varying severity (from a feeling of heaviness). , fatigue in the legs, various degrees of swelling, formation of subcutaneous fatty tissue and skin, dermatitis, eczema and possible formation of venous trophic ulcers).
Doctors describe this pathological condition as polyetiological, as it occurs under the influence of various factors. The main ones are:
- Innate tendency;
- Pregnancy in women;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Overweight;
- Passive lifestyle.
The team of professional phlebologists of the "Doctor Nearby" family clinic network is always ready to help those who want to recover from this disease. The course is selected individually, taking into account all factors. With the use of modern effective techniques, this allows you to achieve the desired results.
Causes and signs of varicose veins
The main pathogenetic mechanisms leading to the development of varicose veins are as follows:
- Increased intravenous pressure, which is primarily determined by the hydrostatic pressure that develops in the vein under the influence of gravity, which is determined by the height of the liquid column, i. e. the distance between the heart and the point of the leg where the measurement takes place. And the pressure inside the body cavities - abdominal or pleural, when increased (pregnancy, excess weight, lifting and carrying heavy objects, etc. ) return of venous blood to the heart deteriorates.
- Relative weakness of the venous wall, which is genetically determined, but can sometimes change as a result of inflammatory processes occurring in the vein.
The interaction of these factors leads to the progressive stretching of the vein, the development of insufficiency of the venous valves, the appearance of reverse blood flow and stagnation in the venous bed.
In the case of long-term exposure to provoking factors, inflammatory processes develop, which during their development affect and weaken the strength of the venous wall of the venous valves.
As a result of all these processes, an abnormal reverse blood flow occurs in the vein, which is called reflux, and venous stasis develops, which leads to the development of subcutaneous fat and dermatitis, which with further progression leads to the appearance of a trophic ulcer.
Symptoms of varicose veins:
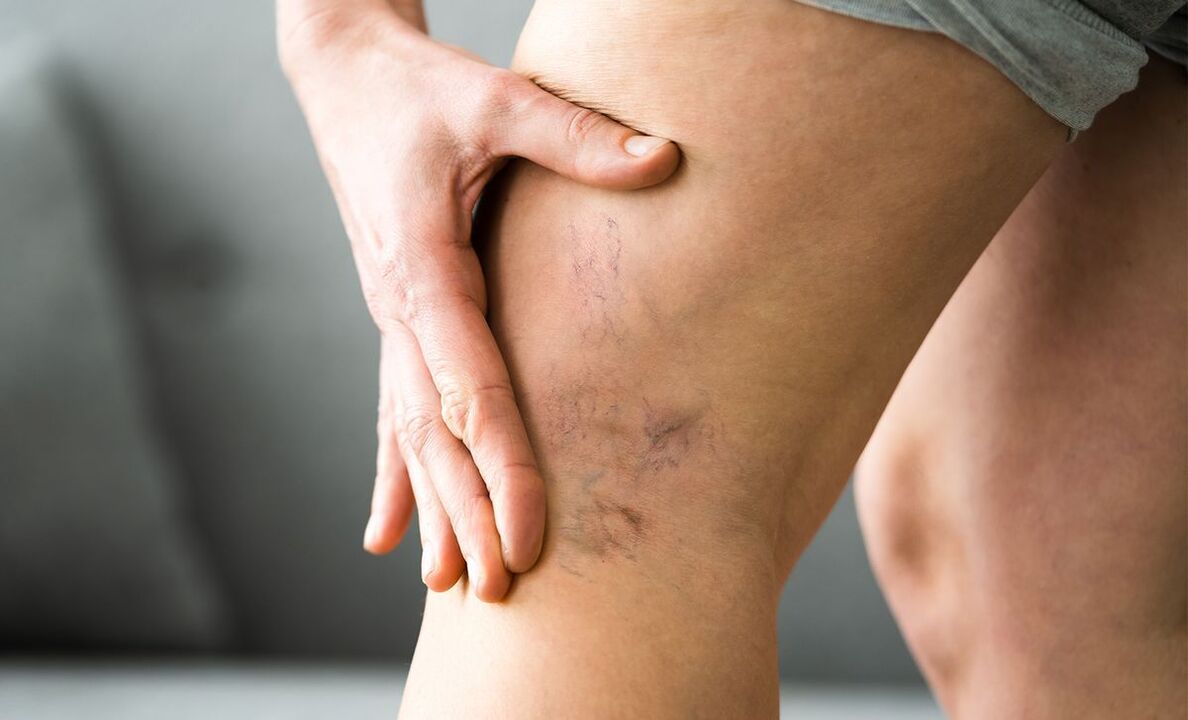
- Visually noticeable expansion and tortuosity of the saphenous veins, in advanced cases - the formation of venous nodes;
- Heaviness, fatigue, feeling of fullness in the calves in the lower limbs;
- Formation of telangiectasia (vascular "stars", "nets");
- Nocturnal cramps of the calf muscles;
- Swelling of the legs and feet;
- Itching, dryness, hyperpigmentation and bluing of the skin
- Appearance of trophic, weeping, poorly healing ulcers.
Risks of varicose veins
Varicose veins on the legs are more of a cosmetic problem in themselves, but they can lead to unpleasant complications: chronic venous insufficiency and inflammation of the vein, which is called acute varicothrombophlebitis. Acute varicothrombophlebitis is a pathological condition that develops as a result of inflammation of the venous wall and the appearance of a blood clot in the lumen. A dangerous complication of varicothrombophlebitis is the continuous growth of the blood clot and its spread into the deep veins. Therefore, this condition requires mandatory medical supervision and treatment, and sometimes leads to emergency surgery. Modern medicine offers many effective techniques that can help eliminate the risk of developing such conditions, but treatment must be started in time.
Classification of varicose veins
There are different classifications of varicose veins which are shown in the table below.
Varicose type/stage/class according to CEAP |
Signs |
The form, extent of the pathology and the complications it led to |
|
C1 |
Damage to intradermal vessels: telangiectasia (colloquially - "spiders", "webs", "stars") and dilated reticular veins. |
C2 |
Dilatation, abnormal tortuosity Damage to the saphenous veins. |
C3 |
Damage to the saphenous veins, accompanied by edema |
C4a С4b |
Hyperpigmentation of the leg (dark brown color) or eczema (skin inflammation, dermatitis) Development of lipodermatosclerosis (inflammation and thickening of the fatty tissue under the skin). |
C5 |
Healed trophic ulcer |
C6 |
"Open" trophic ulcer |
Stages of development of the pathological condition according to Saveljev |
|
Compensation |
There are no symptoms or complaints, during the examination there are dilated veins on one or both lower limbs. |
Undercompensation |
The patient experiences discomfort, which is expressed in swelling and "needles" of the legs, as well as nocturnal spasms of the calf muscles. The condition is accompanied by swelling in the evening, which disappears in the morning. During the examination, varicose veins of the lower limbs are revealed. |
Decompensation |
The discomforts listed above complement inflammatory skin changes and eczema. The skin looks dry and shiny and hyperpigmentation appears. |
The dynamics of the development of varicose veins
Clinical picture of the diseaseit depends on the stage of the disease. At the same time, doctors identify the main clinical symptom that determined the name of the disease - the expansion of the saphenous veins of the lower limbs.
The beginning of the development of the disease
Initially, patients feel heaviness in the legs, fatigue and pain in the legs. During this period, visual signs of pathology are not visible. It often happens that the above symptoms are also absent, so patients do not seek professional medical help. During the examination carried out by the phlebologist, he identifies dilated soft veins, over which the skin has not undergone pathological changes.
Undercompensation stage
During the development of the disease, patients notice pain, swelling occurs when standing or sitting for a long time, which disappears at night. During the examination, the phlebologist notices a slight swelling in the area of the ankle.
The stage of decompensation
The progression of the pathology is expressed in a constant feeling of heaviness in the lower limbs, rapid fatigue and nightly cramps of the calf muscles. In addition, severe itching occurs in the evenings.
During the examination carried out by the doctor, the pronounced expansion of the veins of the lower limbs and the disturbance of the blood flow are revealed. The tension of the veins, adhesion of their walls to the skin, hyperpigmentation, cyanosis, roughness and dryness of the skin can be observed.
The skin lesions appear in the lower third of the leg. First of all, they mean the appearance of brown discoloration of the skin, the development of inflammation - dermatitis or eczema, the appearance of thickening of subcutaneous fatty tissue, against the background of which trophic ulcers later develop and develop.
Diagnosis of varicose veins
Treatment of varicose veinsthey are prescribed after the patient has undergone a comprehensive diagnostic examination, which enables the precise determination of the stage of the disease's development and the pathological changes it leads to. Depending on the situation, it may include the following tests of the lower veins:
- Control;
- Duplex/triplex scanning.
- Examination of some coagulation indicators and thrombophilia markers
Main methoddiagnosis of varicose veinsan ultrasound examination, in addition to which full-scale tests are performed and functional tests are also carried out.
Treatment of varicose veins
Modern phlebology offers many effective methodsmethods of treating varicose veins. They are selected on an individual basis, based on the clinical case and the patient's indications.
Conservative techniques should not be contrasted with surgical techniques, as they are used in combination. Sometimes conservative treatment can be carried out independently, but it is important to understand that it cannot lead to a cure, although it slows down the development of the pathology and has a positive effect on the patient's condition.
Conservative therapy |
|
When should it be used independently? |
|
Solvable problems |
|
Applied techniques |
Compression therapy that reduces the diameter of the veins and eliminates reflux, as well as stimulating the return of venous blood to the heart and lymphatic drainage. During this, elastic bandages and therapeutic compression stockings are used, which the patient wears daily for the rest of his life or until the end of the surgical correction. The use of therapeutic compression stockings correctly and quickly corrects hemodynamic abnormalities in the legs, even whentreatmentvaricose veinsin an advanced stage. |
Drug therapy involves the prescription of pharmacological drugs aimed at eliminating discomfort in the legs or improving blood microcirculation and lymphatic drainage. The most commonly used drugs are:
|
|
Surgical techniques |
|
Phlebectomy |
|
What is this? |
Surgical intervention to remove varicose veins. |
What problems does it solve? |
Normalization of blood flow through the saphenous veins |
Indications |
|
Peculiarities |
The procedure involves removing the affected veins under the skin. |
Period |
60-120 minutes. |
Traumaticity |
Small scars 5-10 cm in the groin and 0. 5-4 cm on the legs. The patient stays in the hospital for 1-7 days. Sick leave for 24 days |
Endovenous laser coagulation/obliteration of varicose veins (EVLK/EVLO) |
|
What is this? |
A technique aimed at removing veins using a medical laser beam. |
Indications |
|
Traumaticity |
Minimal, The operation is performed by venipuncture. It is done on an outpatient basis. |
Characteristics of the recovery period |
Immediately after the operation, the patient should walk for 30-40 minutes. Compression stockings must be worn for at least 2 weeks. Pain is often absent or minimal |
Sclerotherapy |
|
What is this? |
A procedure that involves the introduction of a special substance - sclerosant - into the lumen of the vessel, which causes the formation of a protein-erythrocyte plug with the subsequent disappearance of the vein. |
Indications |
Phlebeurism. |
Peculiarities |
The technique is effective for the treatment of intradermal veins, in other cases - as a supplement for the removal of small residual branches of the main trunks. |
Complications |
Complications are relatively rare. |
Prevention of varicose veins
Prevention includes:
- Wearing compression stockings;
- Maintaining body weight within normal limits;
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- avoid standing for long periods of time;
- A timely visit to the phlebologist in case of family anamnesis or the appearance of symptoms of the disease.
If you still notice the first signs of varicose veins, seek medical help immediately!























